AIRPLANE WEB PAGE

Airplane Design and Structure
Major components of an airplane (fuselage, wings, engines, tail)
Types of wing configurations (delta, swept, straight)
Material science and composite materials in aircraft design
Fuel systems, electrical systems, and hydraulic systems
Civil vs. military aircraft
Commercial airliners (Boeing, Airbus models)
History of flight and early aviation pioneers
Development of the modern airplane
An airplane, also known as an aeroplane, is a powered flying vehicle designed to transport people or cargo through the air. It typically consists of a fuselage (main body), wings, engines, a tail section, and landing gear. Airplanes are among the most significant inventions of the modern era, revolutionizing transportation, commerce, and global connectivity.
The wings of an airplane are crucial for flight. They generate lift as air flows over and under them, allowing the airplane to rise into the sky.


Aircraft Types and Their Uses

Airplane Design and Structure
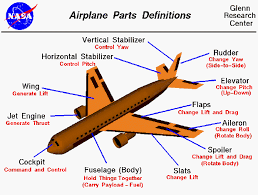
The wings of an airplane are crucial for flight. They generate lift as air flows over and under them, allowing the airplane to rise into the sky. The shape of the wings, called an airfoil, is specially designed to create this lifting force. Most commercial airplanes have two wings, one on each side of the fuselage. Attached to the wings are control surfaces such as ailerons and flaps, which help the pilot control the aircraft’s roll and improve lift during takeoff and landing.
The engines, usually located under the wings or on the rear of the aircraft, provide the thrust needed to propel the airplane forward. Jet engines are most common in modern airplanes, especially in commercial airliners, as they offer high speed and efficiency. Smaller airplanes may use propeller engines.

Introduction to Aviation

History of flight and early aviation pioneers
Development of the modern airplane
The Wright brothers and the first powered flight
Milestones in aviation history
Aerodynamics and the four forces of flight (lift, thrust, drag, weight)
Bernoulli’s principle and Newton’s laws in aviation
Stability and control in flight

Airplanes vary widely in size and purpose. Some are small private planes with just a few seats, while others, like the Boeing 747 or Airbus A380, are massive airliners capable of carrying hundreds of passengers over long distances.
In summary, airplanes are marvels of engineering that combine aerodynamics, physics, and technology to achieve controlled flight. They play a vital role in modern society by connecting people across continents, enabling global trade, and offering rapid response in emergencies and disaster relief operations.

-
Major components of an airplane (fuselage, wings, engines, tail)
-
Types of wing configurations (delta, swept, straight)
-
Material science and composite materials in aircraft design
-
Fuel systems, electrical systems, and hydraulic systems
-
Jet engines: turbofan, turbojet, turboprop, ramjet
-
Propeller-driven aircraft and piston engines
-
Innovations in engine technology and fuel efficiency
-
History of flight and early aviation pioneers
-
Development of the modern airplane
Flight Operations



