MY L.C.D WEB PAGE
An LCD TV (Liquid Crystal Display Television) is a type of flat-panel television that uses liquid crystal display technology to produce images. It has become one of the most popular choices for home entertainment due to its slim design, energy efficiency, and excellent picture quality.
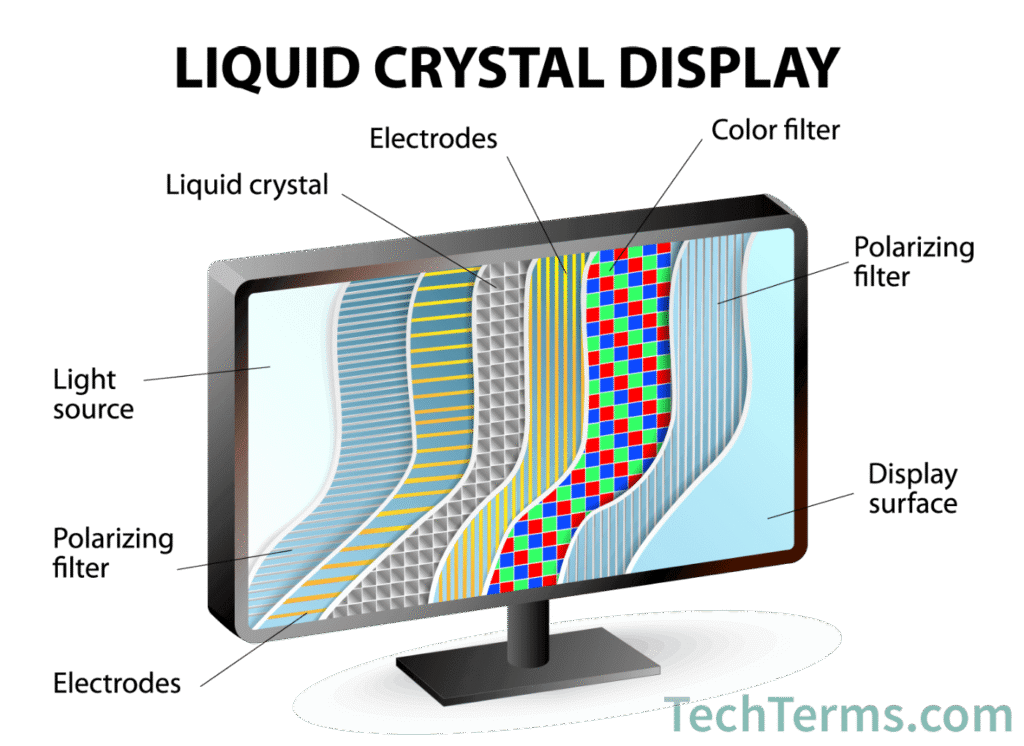
The core of an LCD TV consists of two layers of polarized glass with a liquid crystal solution sandwiched between them. When an electric current passes through the liquid crystals, they align in a way that allows varying amounts of light to pass through, creating images on the screen. Since LCDs do not produce light by themselves, they rely on a backlight—usually LED (light-emitting diode)—to illuminate the screen.
LCD TVs offer several advantages. One of the most notable is their thin and lightweight design, which makes them easy to mount on walls or place on slim stands. They are available in a wide range of screen sizes, from compact models suitable for small rooms to large-screen TVs ideal for home theaters. In terms of image quality, LCD TVs provide sharp, bright, and colorful visuals, making them ideal for watching movies, sports, and playing video games.
Modern LCD TVs come equipped with high-definition (HD), Full HD, and even 4K Ultra HD resolutions, offering stunning clarity and detail. Many models also include features like smart TV capabilities, allowing users to stream content from apps such as Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon Prime directly on the TV without the need for additional devices. Some LCD TVs also support HDR (High Dynamic Range), enhancing contrast and color for a more immersive viewing experience.
LCD vs. OLED vs. QLED
Global Market Trends
Brand Comparisons
Foundations of Display Technology
Modern LCD TVs come equipped with high-definition (HD), Full HD, and even 4K Ultra HD resolutions, offering stunning clarity and detail. Many models also include features like smart TV capabilities, allowing users to stream content from apps such as Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon Prime directly on the TV without the need for additional devices. Some LCD TVs also support HDR (High Dynamic Range), enhancing contrast and color for a more immersive viewing experience.
Another benefit of LCD TVs is their energy efficiency. Compared to older CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) televisions and even some plasma models, LCDs consume less power, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time.
Introduction to Display Technologies
Evolution of Television: From CRT to LCD
The Science of Light and Color

LCD TV Engineering

Manufacturing and Design
How an LCD Works
Backlighting Technologies (CCFL vs. LED)
Panel Types: TN, IPS, VA
Resolution Standards (HD, Full HD, 4K, 8K)
Color Reproduction and Calibration
Response Time and Refresh Rates
Viewing Angles and Contrast Ratios
An LCD TV (Liquid Crystal Display Television) is a type of flat-panel television that uses liquid crystal display technology to produce images. It has become one of the most popular choices for home entertainment due to its slim design, energy efficiency, and excellent picture quality.
The core of an LCD TV consists of two layers of polarized glass with a liquid crystal solution sandwiched between them. When an electric current passes through the liquid crystals, they align in a way that allows varying amounts of light to pass through, creating images on the screen.
Another benefit of LCD TVs is their energy efficiency. Compared to older CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) televisions and even some plasma models, LCDs consume less power, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time.
In conclusion, LCD TVs provide a versatile and affordable option for anyone looking to upgrade their home entertainment system. With their sleek design, high-resolution displays, and smart features, they offer great value and performance for a wide range of users.
An LCD TV (Liquid Crystal Display Television) is a type of flat-panel television that uses liquid crystal display technology to produce images. It has become one of the most popular choices for home entertainment due to its slim design, energy efficiency, and excellent picture quality.



LCD Panel Manufacturing
Chassis Design and Materials
Environmental Considerations
Power Efficiency and Energy Ratings
Quality Control and Testing
Operating Systems (WebOS, Android TV, Tizen, etc.)
Smart Features and Software
Operating Systems (WebOS, Android TV, Tizen, etc.)
Voice Control and AI Integration
Connectivity (HDMI, USB, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth)
Streaming and Smart Features

LCD in Commercial and Industrial Use
Gaming and Entertainment Uses
Future of LCD: Mini-LED, MicroLED
Sustainability in TV Manufacturing
The Role of LCD in the Future of Media
Resolution, Refresh Rates, and Scaling
Applications of LCDs
Controller ICs
HDMI, VGA, LVDS, eDP protocols
Resolution, Refresh Rates, and Scaling
HD, Full HD, 4K, 8K
Consumer electronics
LCD technology has evolved significantly over the years, offering higher resolutions such as Full HD, 4K, and even 8K, improving refresh rates, and enabling touchscreen functionality in smartphones and tablets. Despite the rise of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays, which provide better contrast and color depth, LCDs remain popular due to their affordability and energy efficiency.
In summary, LCDs play a vital role in modern electronics by providing a reliable, efficient, and high-quality visual interface for a wide range of applications.

